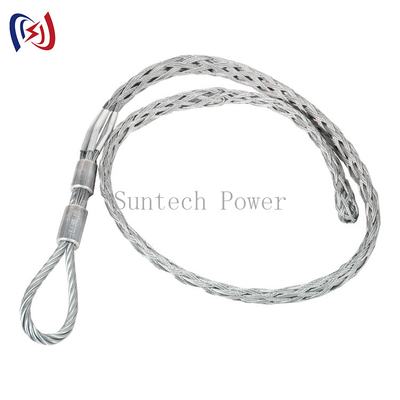
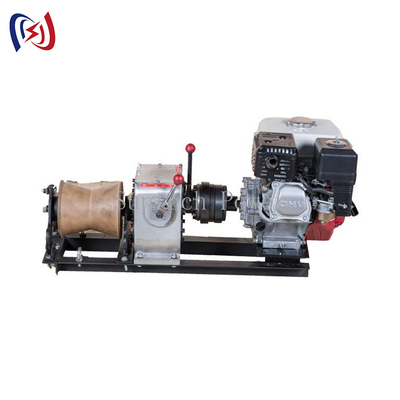
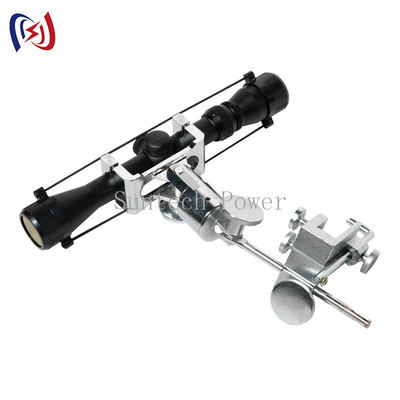
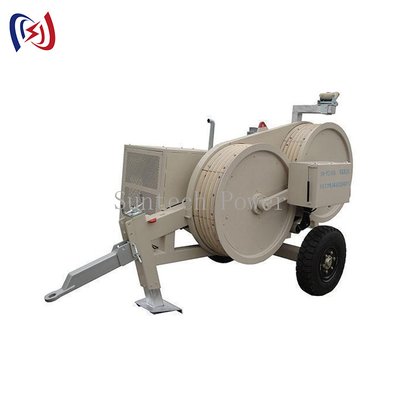
ในสาขาการก่อสร้างและบำรุงรักษาสายไฟฟ้าแรงสูงที่มีความซับซ้อนและมีความเสี่ยงสูง ความสมบูรณ์ของตัวนำไฟฟ้าเป็นสิ่งสำคัญยิ่ง อุปกรณ์ที่เสียหายเพียงเส้นเดียวหรือแกนกลางที่เสียหายอาจนำไปสู่ความล้มเหลวอย่างร้ายแรง การซ่อมแซมที่มีค่าใช้จ่ายสูง และระยะเวลาหยุดทำงานที่ยาวนาน เครื่องมือสำคัญในคลังแสงของช่างไฟฟ้าและผู้รับเหมาสาธารณูปโภคทุกคนคือ Conductor Mesh Sock Joint ซึ่งเป็นอุปกรณ์ที่ดูเรียบง่ายแต่ได้รับการออกแบบมาเพื่อวัตถุประสงค์ที่สำคัญอย่างยิ่ง: เพื่อจับและดึงตัวนำไฟฟ้าอย่างปลอดภัยโดยไม่ก่อให้เกิดความเสียหาย
สำหรับบริษัทวิศวกรรมและทีมงานก่อสร้างที่ทำงานในโครงการส่งและจำหน่ายทั่วเอเชียกลาง ตะวันออกกลาง แอฟริกา อเมริกาใต้ และเอเชียตะวันออกเฉียงใต้ การเลือกอุปกรณ์ดึงที่เหมาะสมถือเป็นการตัดสินใจขั้นพื้นฐาน คู่มือนี้ให้ภาพรวมที่ครอบคลุมและเป็นกลางของข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้า โดยอธิบายถึงการทำงาน ประโยชน์หลัก และปัจจัยสำคัญที่ต้องพิจารณาในระหว่างการจัดซื้อ
หากต้องการสำรวจข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้าที่ทนทานและเชื่อถือได้ซึ่งออกแบบมาสำหรับการใช้งานที่ต้องการ เราขอเชิญคุณเยี่ยมชมหน้าแรกของผลิตภัณฑ์ของเราเพื่อดูข้อมูลจำเพาะโดยละเอียด
การทำความเข้าใจปัญหา: ทำไมคุณไม่สามารถดึงตัวนำไฟฟ้าได้โดยตรง
การดึงตัวนำไฟฟ้า โดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งสาย ACSR (ตัวนำอะลูมิเนียมเสริมเหล็ก) หรือสาย AAAC (ตัวนำโลหะผสมอะลูมิเนียมทั้งหมด) ที่มีน้ำหนักมากในระยะทางไกล จะสร้างแรงดึงมหาศาล การติดเชือกดึงเหล็กหรือสายเคเบิลกว้านโดยตรงกับตัวนำไฟฟ้าไม่ใช่ทางเลือกด้วยเหตุผลหลายประการ:
การบดและการเสียรูป:
สายเคเบิลเหล็กแข็งหรือห่วงจะกัด บด และทำให้เส้นใยอะลูมิเนียมที่อ่อนนุ่มของตัวนำไฟฟ้าเสียรูปอย่างถาวร ทำให้ตัวนำไฟฟ้าอ่อนแอลงอย่างรุนแรง2.
ความเสียหายของเส้นใย:
แรงที่เข้มข้นสามารถทำลายเส้นใยแต่ละเส้น ทำให้เกิดจุดอ่อนที่เกิดความล้มเหลวภายใต้แรงดึงหรือการสั่นสะเทือน
การหมุนและการบิด:
ในระหว่างการดึง เชือกดึงจะบิดและหมุนอย่างหลีกเลี่ยงไม่ได้ หากเชื่อมต่อโดยตรง การบิดนี้จะถูกถ่ายโอนโดยตรงไปยังตัวนำไฟฟ้า ทำให้เกิดการบิด งอ หรือคลายเกลียว—ทำให้ใช้งานไม่ได้
Conductor Mesh Sock Joint เป็นโซลูชันทางวิศวกรรมสำหรับปัญหานี้ ทำหน้าที่เป็นอินเทอร์เฟซที่ปลอดภัย แข็งแรง และให้อภัยระหว่างแรงที่โหดร้ายของกว้านและความแข็งแรงที่ละเอียดอ่อนของตัวนำไฟฟ้า
วิธีการทำงานของ Mesh Sock Joint: หลักการของแรงกระจาย
ข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้า หรือที่เรียกว่าที่จับตาข่ายลวดหรือถุงเท้าตัวนำไฟฟ้า เป็นปลอกยืดหยุ่นที่ทอจากลวดสแตนเลสสตีลหรือเหล็กชุบสังกะสีที่มีความต้านทานแรงดึงสูง การทำงานนั้นเรียบง่ายแต่มีประสิทธิภาพสูง:
1. การสวมใส่:
ถุงเท้าถูกสวมทับปลายตัวนำไฟฟ้า
2. การติดห่วง:
ห่วงหรือห่วงเหล็กถูกรวมเข้าที่ปลายดึงของถุงเท้า โดยมีจุดยึดที่ปลอดภัยในการติดห่วง ข้อต่อหมุน และสุดท้ายคือเชือกดึง
3. การจับ:
เมื่อใช้แรงดึงกับเชือกดึง ปลอกตาข่ายจะรัดรอบวงของตัวนำไฟฟ้าอย่างสม่ำเสมอ
4. การกระจายโหลด:
กุญแจสู่ความสำเร็จคือการกระจายแรงดึงมหาศาลอย่างสม่ำเสมอเหนือพื้นที่ผิวขนาดใหญ่ของตัวนำไฟฟ้า แทนที่จะเป็นจุดสัมผัสเดียวที่สร้างความเสียหาย ตัวนำไฟฟ้าจะถูกโอบล้อมด้วยลวดเหล็กหลายร้อยเส้น โดยแต่ละเส้นจะแบ่งปันภาระงาน สิ่งนี้จะป้องกันการบด การแบน หรือการแตกของเส้นใย
บทบาทของข้อต่อหมุน: ดังที่กล่าวมา เชือกดึงจะหมุน เพื่อป้องกันไม่ให้การหมุนนี้ถูกถ่ายโอนผ่านถุงเท้าตาข่ายและเข้าไปในตัวนำไฟฟ้า จะมีการติดตั้งข้อต่อหมุนเสมอระหว่างห่วงของถุงเท้ากับเชือกดึง ข้อต่อหมุนทำหน้าที่เป็นองค์ประกอบการหมุนแบบเสียสละ ดูดซับแรงบิดทั้งหมด และช่วยให้ตัวนำไฟฟ้าถูกดึงตรงและแม่นยำ
การใช้งานหลักในภาคสนาม
ข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้าเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นสำหรับงานสายไฟเหนือศีรษะที่หลากหลาย:
•
การติดตั้งครั้งแรก: การดึงสายตัวนำใหม่ที่ขึงเหนือช่วงยาวระหว่างเสา
•
การเปลี่ยนตัวนำไฟฟ้า: การถอดตัวนำไฟฟ้าเก่าและดึงตัวนำไฟฟ้าใหม่เข้ามาแทนที่
•
การซ่อมแซมและบำรุงรักษา: การดึงและหย่อนสายไฟที่มีอยู่หลังจากการซ่อมแซมหรือเพื่อแก้ไขการหย่อนคล้อย
•
การฟื้นฟูฉุกเฉิน: การขึงตัวนำไฟฟ้าใหม่หลังจากพายุหรือความเสียหายจากอุบัติเหตุอย่างรวดเร็ว
ความสามารถรอบด้านทำให้เป็นส่วนประกอบหลักในทุกสิ่งตั้งแต่สายจำหน่ายแรงดันต่ำไปจนถึงโครงการส่งกำลังไฟฟ้าแรงสูงพิเศษ
คู่มือสำหรับผู้ซื้อ: ปัจจัยการคัดเลือกที่สำคัญ
การเลือกตาข่ายถุงเท้าที่ไม่ถูกต้องอาจนำไปสู่การลื่นไถล ความเสียหายของตัวนำไฟฟ้า หรือแม้แต่ความล้มเหลวภายใต้ภาระ สำหรับเจ้าหน้าที่จัดซื้อและหัวหน้าช่างไฟฟ้า นี่คือปัจจัยทางเทคนิคและการปฏิบัติที่จำเป็นที่ต้องพิจารณา
1. เส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางของตัวนำไฟฟ้า (ปัจจัยที่สำคัญที่สุด):
ถุงเท้าตาข่ายได้รับการออกแบบมาสำหรับช่วงเส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางของตัวนำไฟฟ้าที่เฉพาะเจาะจงมาก
• ใหญ่เกินไป: ถุงเท้าที่ใหญ่เกินไปสำหรับตัวนำไฟฟ้าจะไม่รัดตัวอย่างถูกต้องและจะลื่นภายใต้ภาระ อาจหลุดออกไปด้วยแรงอันตราย
• เล็กเกินไป: ถุงเท้าที่เล็กเกินไปจะไม่พอดีกับตัวนำไฟฟ้าหรือจะรัดแน่นเกินไป เสี่ยงต่อการทำลายลวดตาข่ายและตัวนำไฟฟ้า
• วิธีแก้ไข: ปรึกษาแผนภูมิขนาดของผู้ผลิตเสมอ วัดเส้นผ่านศูนย์กลางภายนอก (O.D.) ของตัวนำไฟฟ้าของคุณอย่างแม่นยำ และเลือกถุงเท้าที่มีช่วงที่ระบุไว้ซึ่งรวมถึงการวัดนั้น
2. ขีดจำกัดการรับน้ำหนัก (WLL) และความแข็งแรงของวัสดุ:
• WLL: ถุงเท้าคุณภาพทุกชิ้นมีขีดจำกัดการรับน้ำหนักที่ทำเครื่องหมายไว้อย่างชัดเจน สิ่งนี้ต้องสูงกว่าแรงดึงสูงสุดที่คาดว่าจะเกิดขึ้นระหว่างการทำงานอย่างมาก คำนึงถึงน้ำหนักของตัวนำไฟฟ้า ความยาวของการดึง และความลาดเอียง
• วัสดุ: ถุงเท้าทำจากสแตนเลสหรือลวดเหล็กชุบสังกะสีหลายเกรด สแตนเลสสตีลมีความทนทานต่อการกัดกร่อนที่เหนือกว่าสำหรับภูมิภาคชายฝั่งหรือที่มีความชื้นสูง ในขณะที่เหล็กชุบสังกะสีที่มีความต้านทานแรงดึงสูงให้ความแข็งแรงที่แข็งแกร่งสำหรับการใช้งานทั่วไป ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าวัสดุเหมาะสมกับสภาพแวดล้อมในท้องถิ่นของคุณ
3. คุณสมบัติการก่อสร้างและการออกแบบ:
• รูปแบบการถักเปีย: คุณภาพของการทอมีผลต่อความยืดหยุ่นและความแข็งแรง การถักเปียที่แน่นและสม่ำเสมอเป็นสิ่งจำเป็นสำหรับการกระจายภาระอย่างสม่ำเสมอ
• คุณภาพของปลอก/ห่วง: รูสำหรับดึงเป็นจุดเน้นที่สำคัญ ต้องเสริมความแข็งแรงและทำจากส่วนประกอบที่หลอมหรือกลึงเพื่อป้องกันการเสียรูป
• ความยาวของปลอก: ปลอกที่ยาวขึ้นให้พื้นที่ผิวการจับยึดที่มากขึ้น ซึ่งจำเป็นสำหรับการดึงที่หนักกว่าและตัวนำไฟฟ้าที่ใหญ่กว่า
4. ความเข้ากันได้กับข้อต่อหมุน:
ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าห่วงบนตาข่ายถุงเท้ามีขนาดและความแข็งแรงที่เหมาะสมในการจัดการห่วงจากข้อต่อหมุนมาตรฐานของคุณ ห่วงโซ่การเชื่อมต่อทั้งหมด (ถุงเท้า -> ห่วง -> หมุน -> ห่วง -> เชือกดึง) ต้องได้รับการจัดอันดับสำหรับภาระเดียวกัน
5. ความทนทานและอายุการใช้งาน:
• ความต้านทานการกัดกร่อน: สำหรับโครงการในตะวันออกกลาง (ความร้อน ทราย) พื้นที่ชายฝั่ง (ละอองเกลือ) หรือภูมิภาคเขตร้อนชื้น ความต้านทานการกัดกร่อนเป็นสิ่งสำคัญที่สุด
• ความต้านทานการขัดถู: ถุงเท้าจะถูกลากไปบนลูกกลิ้งและอาจเป็นพื้นดิน ถุงเท้าที่ทำมาอย่างดีสามารถทนต่อการใช้งานในทางที่ผิดนี้ได้หลายครั้งก่อนที่จะต้องเปลี่ยน
การลงทุนในข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้าที่มีขนาดและพิกัดที่ถูกต้องเป็นค่าใช้จ่ายเล็กน้อยเมื่อเทียบกับมูลค่าของตัวนำไฟฟ้าที่ป้องกันและค่าใช้จ่ายในการดึงที่ไม่สำเร็จ สำหรับการเลือกถุงเท้าที่ตรงตามเกณฑ์ที่เข้มงวดเหล่านี้ ข้อมูลโดยละเอียดมีอยู่ในเว็บไซต์หลักของเรา
แนวทางปฏิบัติที่ดีที่สุดในการดำเนินงานและความปลอดภัย
• การตรวจสอบ: ตรวจสอบตาข่ายถุงเท้าอย่างละเอียดก่อนใช้งานทุกครั้ง มองหาลวดที่ขาด การบิดเบี้ยว การกัดกร่อน หรือห่วงที่เสียหาย ห้ามใช้ถุงเท้าที่เสียหาย
• การติดตั้ง: ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าถุงเท้าถูกติดตั้งตรงและเต็มที่บนตัวนำไฟฟ้า ปลายตัวนำไฟฟ้าควรจะเรียบเสมอกับปลายถุงเท้า
• การเชื่อมต่อ: ใช้ข้อต่อหมุนเสมอระหว่างถุงเท้ากับเชือกดึง ตรวจสอบให้แน่ใจว่าห่วงทั้งหมดถูกตรึงอย่างถูกต้องและปลอดภัย
• การดึง: ใช้แรงดึงอย่างราบรื่นและค่อยๆ เพื่อให้ถุงเท้ารัดตัวรอบตัวนำไฟฟ้าอย่างสม่ำเสมอ
• การปลดระวาง: ถุงเท้าตาข่ายเป็นของที่สึกหรอ ปลดระวางตามแนวทางของผู้ผลิตหรือเมื่อมีสัญญาณของการสึกหรออย่างมีนัยสำคัญ
บทสรุป: ผู้พิทักษ์ความสมบูรณ์ของตัวนำไฟฟ้าข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้าตัวนำไฟฟ้าเป็นผลงานชิ้นเอกของวิศวกรรมเชิงปฏิบัติ มันแก้ปัญหาที่สำคัญด้วยโซลูชันที่สง่างาม มีประสิทธิภาพ และนำกลับมาใช้ใหม่ได้ สำหรับบริษัทสาธารณูปโภคและผู้รับเหมา ไม่ได้เป็นเพียงเครื่องมือเท่านั้น แต่เป็นกรมธรรม์ประกันภัยสำหรับสินทรัพย์ที่มีค่าที่สุดบางส่วนบนโครงข่ายไฟฟ้า
ด้วยการทำความเข้าใจหลักการเบื้องหลังการทำงานและการเลือกอย่างชาญฉลาดตามขนาดตัวนำไฟฟ้า ข้อกำหนดด้านภาระงาน และสภาพแวดล้อม ทีมงานสามารถดำเนินการดึงได้อย่างมั่นใจ มีประสิทธิภาพ และที่สำคัญที่สุดคือความปลอดภัย
เพื่อให้ทีมงานของคุณมีข้อต่อตาข่ายถุงเท้าที่แข็งแกร่งและเชื่อถือได้ซึ่งจำเป็นสำหรับการติดตั้งตัวนำไฟฟ้าที่ไร้ที่ติ เราขอแนะนำให้คุณเรียกดูแคตตาล็อกผลิตภัณฑ์ที่ครอบคลุมของเราซึ่งมีอยู่ในเว็บไซต์ของเรา เลือกอย่างชาญฉลาดเพื่อการปกป้องและประสิทธิภาพ

 ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร!
ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร! กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ!
กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ!  ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร!
ข้อความของคุณจะต้องอยู่ระหว่าง 20-3,000 ตัวอักษร! กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ!
กรุณาตรวจสอบอีเมลของคุณ! 










